Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA) is a group of chemicals that are derived from fatty acid linoleic which is common in meat and dairy products.
Given the fact that this is acid is not produced by the body naturally, we must acquire it from food or other dietary supplements. It was readily consumed by humans in the earlier times, through a diet rich in meat and dairy products, but ever since the changes in cattle farming techniques which resulted in the cattle consuming more grain than grass, there has been a reduction of about 3-5 times in the amount of CLA they produce. On top of that, there have also been changes in our own diets and the end result being reduced consumption of CLA. Even though CLA is not critical for our bodies to function, due to its reported health benefits, it is becoming ever more popular.
 In 1979, researchers first noticed the potential of an extract in beef which appeared to contain anti-carcinogenic qualities. In 1987, the extract was identified as CLA and following this discovery, numerous scientific studies were conducted looking at how CLA affects the body. Results were varied, but some results showed that it might help reduce body fat deposits aswell as help improve immune function. Some even suggested that it may lower the risk of cancer and cardiovascular disease.
In 1979, researchers first noticed the potential of an extract in beef which appeared to contain anti-carcinogenic qualities. In 1987, the extract was identified as CLA and following this discovery, numerous scientific studies were conducted looking at how CLA affects the body. Results were varied, but some results showed that it might help reduce body fat deposits aswell as help improve immune function. Some even suggested that it may lower the risk of cancer and cardiovascular disease.
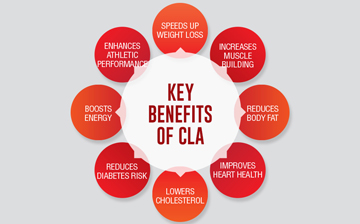
In summary, possible benefits of CLA may include:
- Increasing metabolic rate
- Decreasing body fat deposits
- Enhancing muscle growth
- Lowering cholesterol and triglycerides
- Limits food-induced allergic reactions
- Improving immune function
However, more research is needed to rate the efficacy of CLA for potential consumers. The majority of studies on CLA are conducted on animals, and therefore, a substantial number of studies show that the effects it has on animals, which are not always the same for humans.
Weight loss
In terms of weight loss, supplements that contain CLA have been promoted as a powerful natural weight loss tool. When used on mice, CLA supplementation produced significant decreases in body mass. However, in human studies, the results are far less definitive, so as yet these claims remain inconclusive. In studies that looked at reducing body fat in obese participants, a dose of 1.8 to 7 grams per day has been used. Doses of more than 3.4 grams did not seem to provide any additional benefit.
All in all, there is definitely mounting evidence tp support the benefits of CLA for losing weight and building lean body mass. The message we are getting is to look out for a high grade, quality supplement.
Do you want to find an effective CLA treatment? Check out our top rated CLA products